Intro.
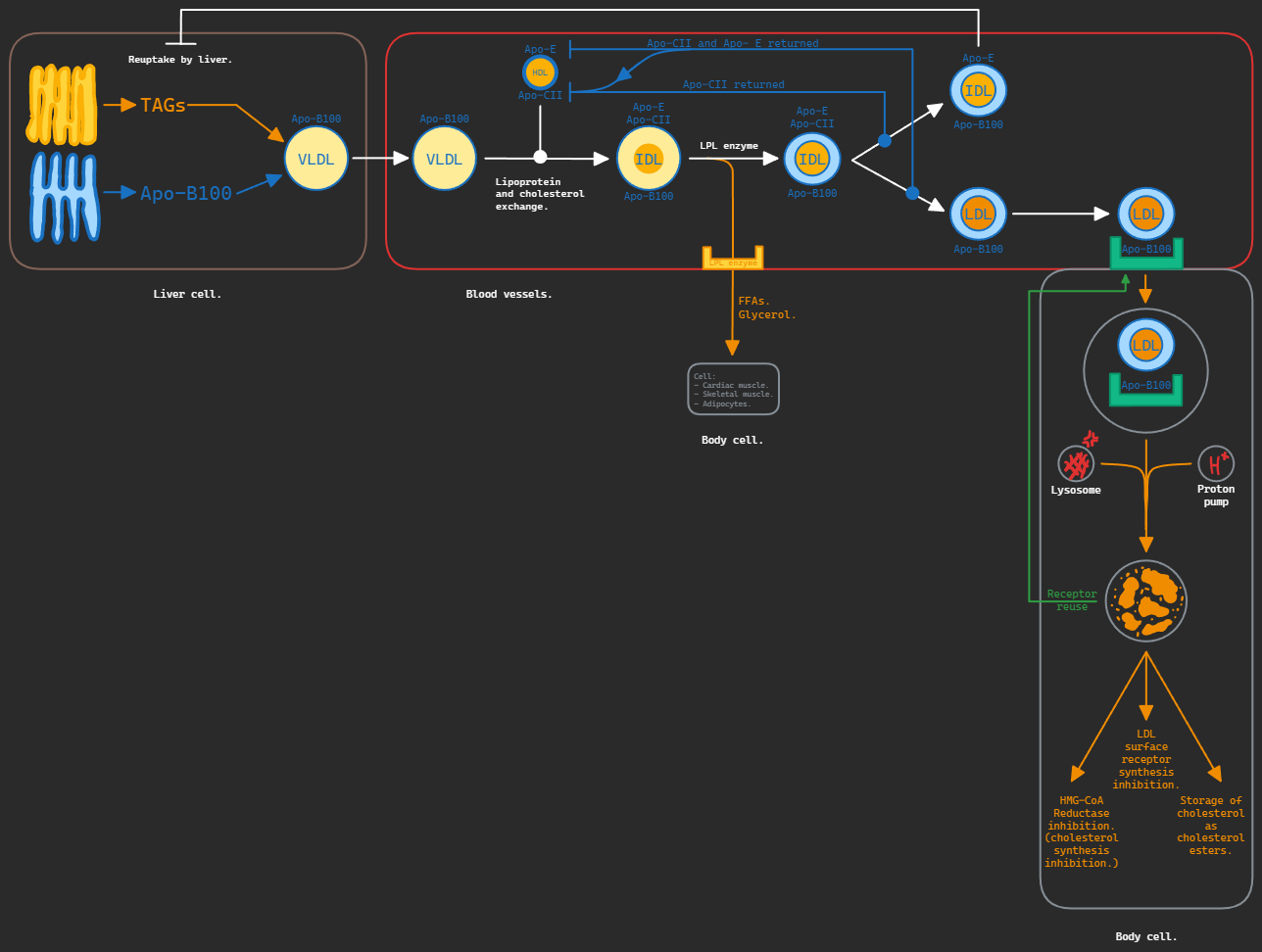
Like chylomicrons, VLDLs transfer TAGs to the tissues. They differ, however, in the place the pick up their TAGs from. While chylomicrons transported TAGs from the intestines to the tissues, VLDLs transport TAGs from the liver to the tissues.
VLDLs.
They are assembled in the liver and carry TAGs (mainly) and cholesterol, etc…
VLDL assembly and modification.
After synthesized TAGs are made, they are loaded onto the VLDL molecules. VLDLs have Apo-B100 apolipoprotein (specific to VLDLs). Then VLDLs are secreted directly into the blood stream (in comparison with chylomicrons, which were released in the lymphatics first). Once they reach the blood, circulating HDL gives it Apo-CII and Apo-E lipoproteins.
Circulating VLDL modification.
As VLDL passes through the circulation, it loses TAGs causing VLDLs to become smaller and denser. Apo-CII and Apo-E are then returned to HDL. VLDLs also exchange some TAGs with HDL for some cholesterol esters, thus it is now smaller, denser, and composed mainly of cholesterol. It becomes IDL (VLDL remanent) then fully becomes LDL.
LDLs.
After VLDLs have been modified (losing Apo-CII & E, retaining Apo-B100), they become LDLs and carry cholesterol and its esters (mainly) and TAGs.
LDL endocytosis.
Apo-B100 is recognized by tissue cell LDL receptors causing the process of endocytosis to begin. LDL-receptor complex is internalized by endocytosis. The clathrin coat towards the cytosolic side is lost, allowing fusion of multiple VLDLs in one vesicle, forming an endosome. LDLs are released from their receptors which exit the vesicle and are reused. LDLs are broken down, releasing FFAs and cholesterol into the cell.
Effects of cholesterol inside the cell.
- Inhibition of HMG-CoA-Reductase, inhibiting cholesterol synthesis.
- inhibition of LDL surface receptor synthesis, inhibiting cholesterol uptake.
- If cholesterol is not required immediately it is stored as cholesterol esters by ACAT enzyme.
Cholesterol and macrophages.
Macrophages possess “scavenger receptors” which are capable of cholesterol uptake from LDLs. The scavenger receptors are NOT down-regulated as a response to cholesterol uptake, which defies effect number 2 above, causing accumulation of cholesterol inside macrophages creating “foam cells” which are major atherosclerotic factors.
.-20240430062019906.png)