Intro.
The head and neck are supplied by the carotid and vertebral arteries.
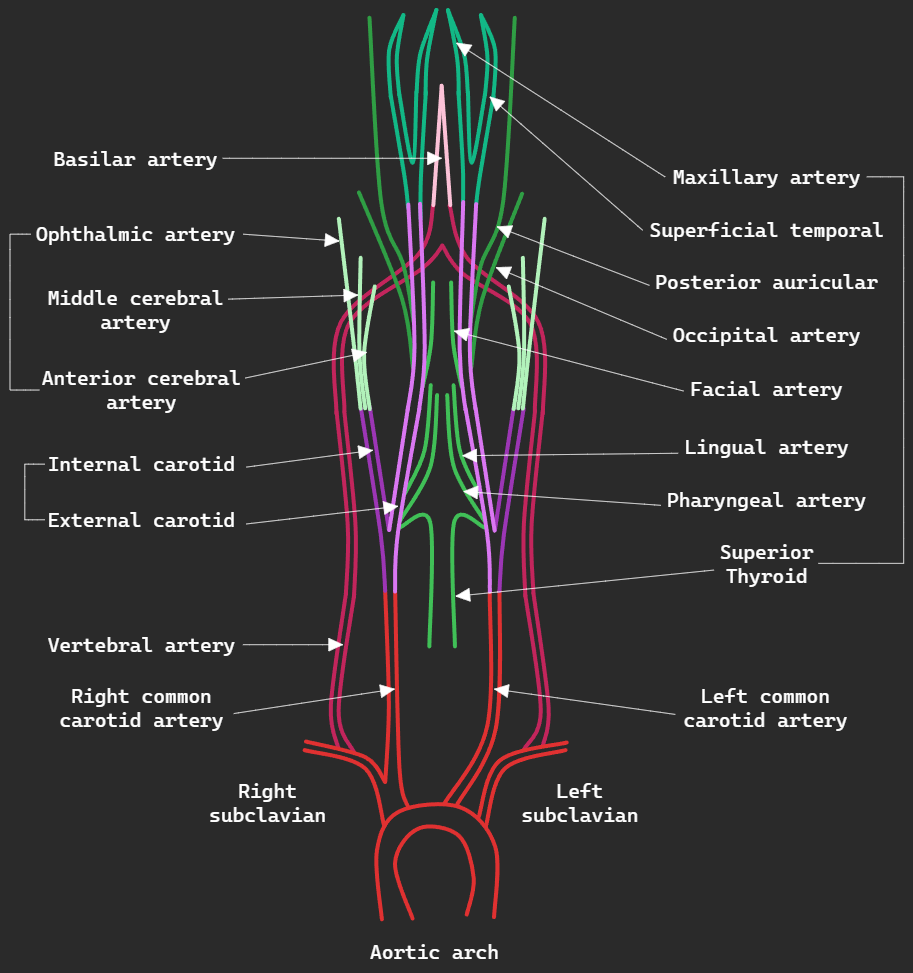
Carotid arteries.
Common carotid arteries.
< Origin >
The right and left common carotid arteries differ in their origin. The right common carotid arises from the brachiocephalic trunk (at the level of the right sternoclavicular joint). The left arises directly from the aortic arch.
< Course >
They ascend up the neck without giving off any branches, at the level of the thyroid cartilage the common carotid arteries split into internal and external carotid arteries. They are slightly dilated creating the carotid sinus.
External carotid artery.
< Origin >
The external carotid artery arises from the common carotid bifurcation at the level of thyroid cartilage (@C4).
< Course >
Travels up the neck posterior to the mandibular neck, anterior to lobule of ear.
< Branches >
- From the carotid triangle.
- Superior thyroid artery.
- Ascending pharyngeal artery.
- Lingual artery.
- Facial artery.
- Occipital artery.
- Posterior auricular artery.
- Terminal branches.
- Maxillary artery.
- Superficial temporal artery.
< End >
External carotid artery ends inside the parotid gland, branching off into superficial temporal artery and maxillary artery.
Internal carotid artery.
< Origin >
< Course >
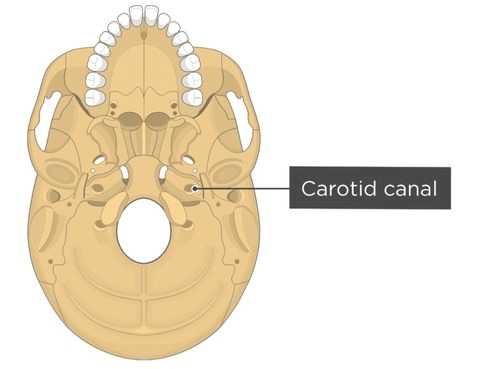
Continues through carotid sheath the enter the carotid canal of temporal bone. In the cranial cavity the internal carotid arteries anastomose with the vertebral arteries forming the circle of Willis.
< Branches >
- Ophthalmic artery (supplying the eye and forehead.)
- Middle cerebral artery (supplying the brain.)
- Anterior cerebral artery (supplying the brain.)
< End >
Anastomoses with vertebral arteries.
Vertebral arteries.
< Origin >
As mentioned before, the vertebral arteries arise from part-1 of subclavian arteries (which gave rise to the vertebral arteries as well as the thyrocervical trunk {unimportant.})
< Course >
After splitting from the subclavian artery, they ascend the posterior side of the neck through the transverse cervical foramen.
< Branches >
- none.
< End >
The vertebral arteries enter the cranial cavity through the foramen magnum and combine to form the basilar arteries, supplying the brain.